The AI Automation Revolution is Already Here
It’s no longer a question of if AI will change business processes, but how fast. We’ve moved past the novelty phase of generating text and images into a new era of practical, tangible automation. The numbers back this up: According to a global survey by McKinsey, a staggering 78% of organizations now report using AI in at least one business function. This isn’t just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how work gets done. What’s driving this rapid adoption is the power of Large Language Models (LLMs) to understand, reason, and act, turning once-complex manual tasks into streamlined, intelligent workflows. This article explores seven LLM-powered AI automation tools that you might not know about, moving from user-friendly platforms to the powerful developer frameworks that are reshaping industries. You will learn not just what these tools are, but how they are fundamentally changing the nature of automation itself.
What Exactly is AI Automation? (And How LLMs Changed the Game)
For years, “automation” in business meant Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Think of RPA as a digital worker that follows a very strict, pre-defined script: click here, copy this field, paste it there. It’s incredibly efficient for repetitive, structured tasks but breaks the moment the process deviates. If a website button moves or an invoice format changes, the traditional bot gets stuck.
LLM-powered AI automation is fundamentally different. Instead of just following a script, it understands context. Thanks to their training on vast amounts of text and code, LLMs can handle unstructured data, like emails, documents, and support tickets, and make decisions. This is the leap from “doing” to “understanding.” The LLM doesn’t just copy text from an invoice; it understands what an “invoice number” or “due date” is, no matter where it appears on the page. This ability to interpret and act on information transforms automation from a rigid, brittle system into a flexible, intelligent one.
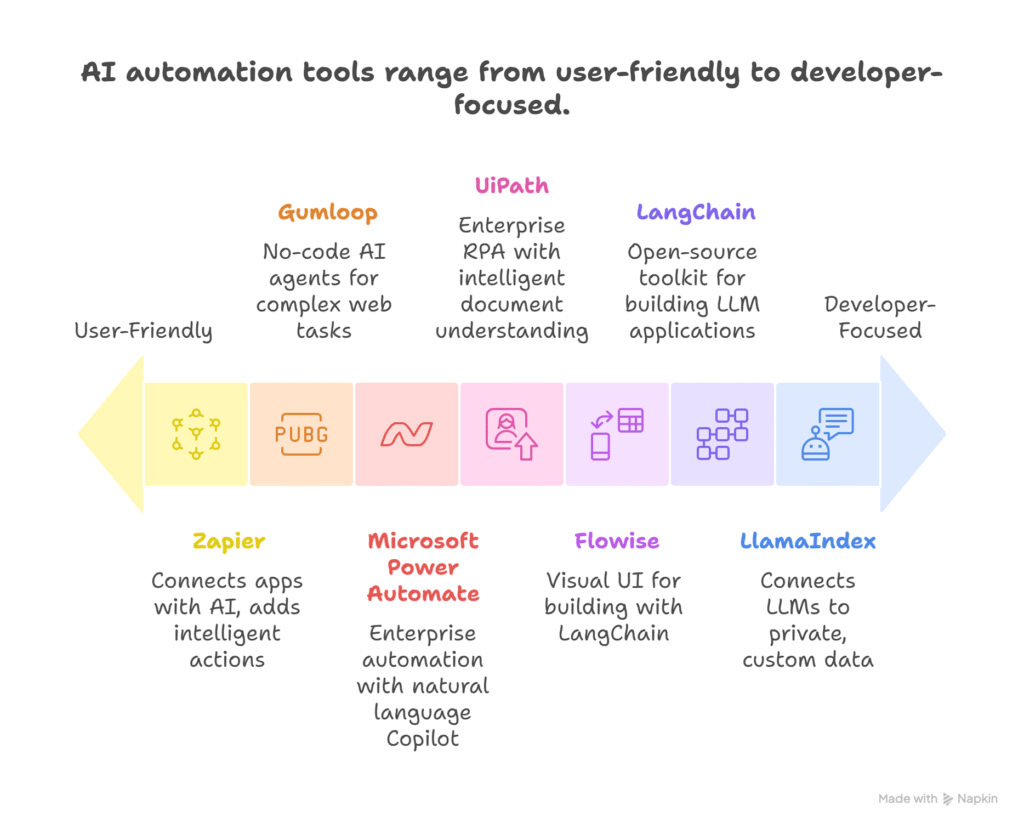
Tool 1: Zapier – The OG of Automation Gets an AI Brain
Many know Zapier as the go-to tool for connecting web apps. Its classic “trigger-action” model (if this happens in App A, do that in App B) has saved countless hours. But with the integration of AI, Zapier is evolving from a simple connector into an intelligent workflow engine.
How it Works: Beyond Triggers to Intelligent Actions
Zapier now embeds AI capabilities directly into its workflows. You can add steps that summarize text, classify customer feedback, draft email responses, or even format data based on natural language instructions. Instead of just passing data from one app to another, Zapier can now analyze and transform that data mid-flight. According to Zapier’s documentation, their goal is to allow natural language to power integrations, letting you build complex workflows without needing to be a programmer.
Practical Example: Automating Customer Feedback Analysis
Imagine you receive customer feedback through a Typeform survey. In the past, you might have set up a Zap to simply copy the feedback into a Google Sheet. Now, you can build a multi-step “Zap” that:
- Triggers when a new Typeform entry is submitted.
- Sends the feedback text to a Zapier AI action to determine if the sentiment is positive, negative, or neutral.
- Based on the sentiment, it routes the feedback. Negative feedback gets sent to a Slack channel for the support team and creates a ticket in Zendesk. Positive feedback gets added to a “Testimonials” spreadsheet.
Tool 2: Gumloop – For When Zapier Isn’t Enough
While Zapier excels at connecting well-defined APIs, Gumloop is designed for the messier, more complex tasks that happen outside of neat integrations. It’s a no-code platform built from the ground up for creating AI agents that can interact with the web and automate multi-step processes.
What Makes it Different: AI Agents and Web Scraping
Gumloop’s core strength lies in its ability to build “flows” using a drag-and-drop interface where each step, or “node,” can be a powerful AI action. This includes reading PDFs, extracting data from websites, and making decisions based on the information it finds. One of its key features is a browser extension that can record your actions on a website and turn them into an automated workflow, allowing it to work with sites that don’t have an API.
Practical Example: Building a Competitor Monitoring Agent
Let’s say you want to track when your competitors launch new features. You could build a Gumloop agent that:
- Visits a list of competitor websites every 24 hours.
- Scrapes the text from their “What’s New” or blog pages.
- Feeds that text into an LLM node to summarize the updates and identify if a new feature was announced.
- If a new feature is detected, it sends a summary to your team’s Slack channel and adds the details to a Notion database for competitive analysis.
Tool 3: Microsoft Power Automate – Enterprise-Grade AI Automation
For organizations embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem, Microsoft Power Automate is a powerhouse for AI automation. It integrates deeply with Office 365, Dynamics 365, and Azure, bringing sophisticated automation capabilities to everyday business applications.
The Power of Copilot: Natural Language to Workflow
The game-changer for Power Automate is the integration of Copilot. Users can now describe the workflow they want in plain English, and Copilot will build the automation flow for them. This drastically lowers the barrier to entry, allowing business users without technical expertise to create powerful automations. This natural language-to-workflow capability is a central part of Microsoft’s strategy to embed AI across its entire product suite.
Practical Example: Streamlining Invoice Processing
A common business process is handling invoices that arrive as PDF attachments in Outlook. A Power Automate flow can be designed to:
- Trigger whenever an email with an attachment arrives in a specific inbox.
- Use AI Builder (part of the Power Platform) to scan the PDF attachment and extract key information like invoice number, vendor name, amount, and due date.
- Create a new item in a SharePoint list or an entry in a financial system with the extracted data.
- Send a notification to the appropriate manager in Microsoft Teams for approval.
Tool 4: UiPath – Bringing LLMs to Enterprise RPA
UiPath has long been a leader in the traditional RPA space. Now, the company is heavily investing in AI to make its automation “bots” smarter and more capable of handling complex, cognitive tasks. Their platform combines the reliability of RPA with the intelligence of generative AI.
From Rigid Bots to Intelligent Document Processing
Where traditional RPA needs structured data, UiPath’s AI-infused platform can now perform “intelligent document understanding.” It can process unstructured documents like contracts or purchase orders, extracting relevant information and making decisions based on the content. UiPath’s Autopilot feature uses generative AI to help developers build automations faster and allows business users to manage processes using natural language.
Practical Example: Automating HR Onboarding
The HR onboarding process often involves numerous documents and systems. An AI-powered UiPath workflow can:
- Monitor an HR inbox for a signed offer letter from a new hire.
- Extract the new hire’s name, start date, and role from the letter.
- Automatically create a user account in Active Directory, a profile in the HR system, and a hardware request in ServiceNow.
- Generate and send a welcome email to the new hire with first-day instructions.
For the Builders: The Frameworks Behind the Magic
The tools above provide user-friendly interfaces for building AI automations. But for developers who need more control and customization, a set of powerful frameworks has emerged that act as the building blocks for creating custom LLM-powered applications.
Tool 5: LangChain – The Developer’s Toolkit for LLM Chains
LangChain is an open-source framework that makes it easier for developers to build applications with LLMs. At its core, it provides a standard way to “chain” together different components, like an LLM, a data source, and a set of instructions. It allows an LLM to interact with its environment, connect to external data sources, and have memory of past interactions.
Tool 6: Flowise – The Visual Way to Build with LangChain
For those who want the power of LangChain without writing extensive code, Flowise offers a solution. It’s an open-source, visual tool for building custom LLM workflows using a drag-and-drop interface. Each node on the canvas represents a LangChain component, allowing you to visually connect LLMs, tools, and data loaders to create sophisticated AI agents and applications. This makes the process of prototyping and building LLM applications much faster.
Tool 7: LlamaIndex – Giving Your Automation Long-Term Memory
One of the biggest challenges for LLMs is that they only know what they were trained on. They don’t know about your company’s internal documents, data, or recent emails. LlamaIndex is a framework designed to solve this problem.
How RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) Works
LlamaIndex specializes in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). This is a technique that connects an LLM to your private data sources. It works by:
- Indexing: LlamaIndex “ingests” your documents (PDFs, Notion pages, etc.) and converts them into a searchable format called vector embeddings.
- Retrieving: When you ask a question, it searches your indexed data to find the most relevant information.
- Generating: It then passes your question and the relevant information to an LLM, instructing it to generate an answer based only on the provided context.
Practical Example: Building an Internal Knowledge Bot
You could use LlamaIndex to build a chatbot for your company’s internal wiki, which is hosted in Confluence. The bot would be able to answer specific questions from employees, like “What is our policy on remote work?” or “How do I set up my development environment?” by retrieving the relevant pages from Confluence and generating a summarized, accurate answer. This turns a static knowledge base into an interactive, intelligent assistant.
Common Challenges and What to Watch For
While the potential of AI automation is immense, it’s not without its challenges. Inaccuracy remains a significant risk; LLMs can still make mistakes, a phenomenon often called “hallucination.” A McKinsey report notes that this is one of the most recognized risks of generative AI. Organizations must implement human oversight and robust testing to validate the outputs of their automated workflows. Cost can also be a factor, as running complex AI models at scale can be expensive. Finally, security and data privacy are paramount, especially when connecting AI tools to sensitive internal data.
The Future is Agentic: What’s Coming Next
The next frontier in AI automation is the rise of “agentic workflows.” Coined by AI researcher Andrew Ng, this refers to a more iterative and autonomous approach. Instead of a linear, one-shot process, an AI agent can be given a goal and then plan a series of steps, use tools, reflect on its progress, and even critique its own work to achieve the goal. For example, you could ask an AI agent to “produce a market research report on the electric vehicle industry.” The agent might independently decide to search the web for recent news, analyze sales data from a connected database, and generate charts before writing the final report. This shift from executing predefined tasks to autonomous problem-solving is what makes the future of AI automation so exciting.
Quick Takeaways
- AI Automation is Mainstream: A 2024 McKinsey survey shows 78% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function.
- Beyond Simple Rules: Unlike traditional RPA, LLM-powered automation understands context and can handle unstructured data like emails and PDFs.
- User-Friendly Tools Exist: Platforms like Zapier and Gumloop allow non-developers to build intelligent workflows with no-code interfaces.
- Enterprise-Ready Solutions: Microsoft Power Automate and UiPath offer robust, scalable AI automation for large organizations, integrating with existing systems.
- Developer Frameworks Offer Power: For custom solutions, open-source tools like LangChain and LlamaIndex provide the building blocks for creating bespoke AI applications.
- Data is Key: LlamaIndex uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to connect LLMs to your private data, ensuring answers are accurate and relevant.
- The Future is Agentic: The next wave of automation will involve AI agents that can plan, reason, and act autonomously to achieve complex goals.
Conclusion
We are at a turning point where AI is moving from a tool for specific tasks to a platform for end-to-end process automation. The key development is the ability of LLMs to bridge the gap between unstructured human communication and structured digital processes. This has given rise to a new class of tools that are more flexible, intelligent, and accessible than ever before. One of the biggest lessons learned is that the most effective AI automation doesn’t try to replace humans, but rather augments their capabilities by handling the repetitive, data-intensive parts of their work. The emerging trend of agentic AI promises even greater autonomy, where systems can tackle complex goals with minimal human intervention. As a next step, businesses should identify a high-value, low-complexity manual process within their organization and experiment with one of these tools to build a proof-of-concept. Starting small and demonstrating value is the best way to begin harnessing the power of this transformative technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is AI automation?
- AI automation uses artificial intelligence, particularly machine learning and large language models, to perform tasks that traditionally required human intelligence and intervention. Unlike traditional automation that follows rigid rules, AI automation can handle unstructured data, understand context, and make decisions to manage complex workflows.
- How do LLMs automate tasks?
- LLMs automate tasks by understanding natural language instructions and data. They can read and interpret text from emails, documents, or websites, extract relevant information, summarize content, classify sentiment, and then trigger actions in other software applications. This allows them to automate processes that involve unstructured data, which was a major limitation of older automation technologies.
- Which AI automation tool is best for marketing?
- For marketing, a tool like Gumloop or Zapier with AI features can be very effective. Gumloop is excellent for tasks like scraping competitor websites or social media for insights. Zapier’s AI-powered workflows can automate lead nurturing sequences, sentiment analysis of customer feedback from surveys, and drafting personalized email campaigns.
- What are the limitations of AI automation?
- The primary limitations include the potential for inaccuracies or “hallucinations” where the AI generates incorrect information. There are also concerns about the cost of running large models at scale, data privacy and security when connecting to internal systems, and the need for human oversight to ensure quality and handle exceptions.
- How much does an AI automation tool cost?
- Costs vary widely. No-code platforms like Zapier and Gumloop often have tiered subscription plans based on usage, ranging from free or low-cost tiers for individuals to hundreds or thousands of dollars per month for businesses. Enterprise-grade platforms like UiPath and Microsoft Power Automate are typically priced based on the number of users and the scale of automation, often involving custom enterprise licensing.




